Integrated circuits are the foundation of nearly every modern electronic device. Whether you’re learning how a timer circuit functions or exploring digital logic, understanding integrated circuits (ICs) is essential. This guide explains what an IC is, how it works, and introduces common types such as the 555 timer, LM3914, and field programmable gate arrays.
Table of Contents
What Is an Integrated Circuit?
An integrated circuit (IC) is a small semiconductor chip that contains multiple electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors. These components are embedded onto a single piece of silicon, forming a compact and efficient electronic circuit.

ICs have revolutionized electronics by reducing size, cost, and power consumption while increasing reliability. This is because they replace multiple individual or discrete components with one package.
Also known as IC chips, integrated circuits come in various forms, from simple logic gates to complex microcontrollers and digital signal processors.
Common Types of Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits are categorized by function and complexity. Here are some of the most common types:
- Logic ICs:
- The 7400 series (TTL logic) includes basic logic gates, flip-flops, counters, and shift registers.
- The 4000 series (CMOS logic) offers similar functionality with higher noise immunity and lower power consumption.
- Microcontrollers (MCUs):
Compact systems on a chip that include a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals. Used in embedded systems such as appliance control boards, IoT devices, and automotive electronics. - Microprocessors:
General-purpose CPUs found in personal computers, servers, and some high-end embedded systems. Unlike microcontrollers, microprocessors typically require external memory and peripheral chips. - Analog ICs:
Include operational amplifiers, voltage regulators, and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), which process continuous signals. - Digital Signal Processors (DSPs):
Specialized for high-speed numeric processing tasks such as audio, image, and communication signal processing.
Each type serves a specific role in modern electronics, and many devices today rely on multiple IC types working together within a single system.
What Is an IC and How Does It Work?

An IC works by integrating a complete electronic function into a miniature chip.
Depending on the design, the IC may perform analog, digital, or mixed-signal operations.
Commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial devices, ICs handle everything from timing to voltage regulation.
There are two broad types of integrated circuits:
- Analog ICs: Operate with continuous signals (e.g., amplifiers, voltage regulators).
- Digital integrated circuits: Work with binary data (e.g., logic gates, microprocessors, memory ICs).
Popular Examples of Integrated Circuits
Some integrated circuits are so widely used that they have become standard components in many electronic projects. A few notable examples follow below.
555 Timer
The 555 timer is a popular timer IC used for generating precise time delays and oscillations. It can operate in monostable, astable, or bistable modes.
Key Uses:
- LED blinkers
- Pulse width modulation (PWM)
- Audio tone generators
The image below shows the internal diagram and pin functions of a 555 timer IC and was taken from the 555 timer IC datasheet.

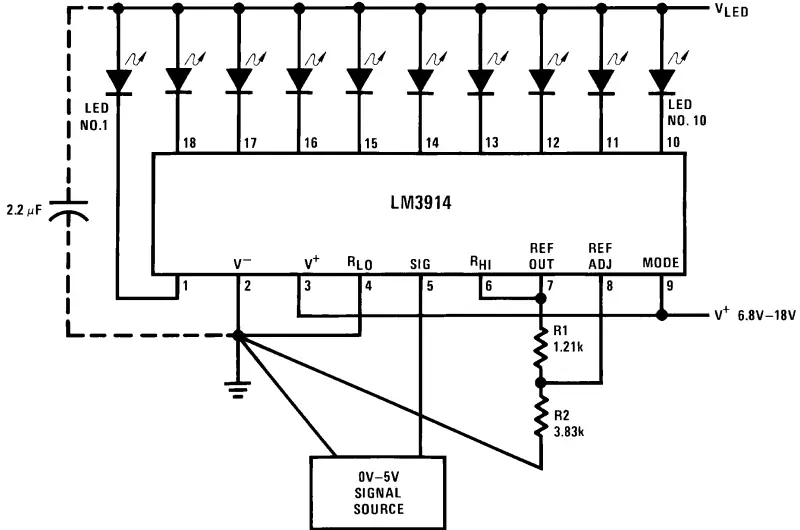
LM3914
The LM3914 is an analog IC used to drive LED bar graphs. It converts an analog voltage into a corresponding LED output level.
Texas Instruments (TI) officially lists the LM3914 as obsolete, and it has been discontinued from active production. TI was the original and main manufacturer, however some companies, mostly in Asia, still manufacture LM3914-compatible ICs. Examples are:
- HT3914 – Manufactured by Holtek
- Unbranded LM3914 clones – Available from suppliers like AliExpress, LCSC, and some eBay sellers.
- UM3914 – Found in some older documentation from Unisonic Technologies.
Caution: The electrical characteristics of clones may differ slightly, so always review the datasheet and test thoroughly for critical applications.
Applications:
- Battery level indicators
- Signal strength meters
- Volume level displays
Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)
A field programmable gate array is a highly flexible digital IC. It can be programmed by the user to implement custom logic circuits.
Common Uses:
- High-speed signal processing
- Custom digital logic
- Prototyping complex systems
Several major manufacturers produce FPGAs:
- AMD Xilinx – Known for its Artix, Spartan, and Zynq FPGA families. Xilinx was acquired by AMD in 2022.
- Intel (formerly Altera) – Offers the popular MAX and Stratix FPGA ranges. Intel acquired Altera in 2015.
- Lattice Semiconductor – Specializes in low-power FPGAs such as the iCE40 and MachXO series. See www.latticesemi.com.
- Microchip (Microsemi) – Provides radiation-tolerant and low-power FPGAs, including the IGLOO and SmartFusion families. Explore www.microchip.com.
These manufacturers offer development tools, IP cores, and documentation to support a wide range of FPGA applications from simple logic designs to advanced embedded systems.
Tips for Integrated Circuits
- Handle with care: IC pins are fragile and easily bent. In addition, many devices can be damaged by static electricity. Always use anti-static wrist straps when handling ICs.
- Read datasheets: Datasheets provide essential information such as pin configuration, operating voltage, and timing diagrams.
- Use sockets (where possible): Inserting ICs into sockets instead of soldering them directly makes replacement easier. The image below shows integrated circuits plugged into sockets on the left and some directly soldered to the circuit board on the right. These are through-hole mounting ICs.
- Mind power supply: Ensure the IC receives a stable and appropriate power supply to prevent malfunction or damage.
- Proper orientation: Double-check IC orientation before powering the circuit to avoid reversed connections.

Did You Know About Integrated Circuits?
- The first integrated circuit was created in 1958 by Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments.
- ICs made space exploration possible; they were crucial in the Apollo missions.
- A single modern microprocessor can contain over a billion transistors on one chip.
- The 555 timer has been in continuous production since 1972 and remains one of the most used ICs ever.
Frequently Asked Questions About Integrated Circuits
What is an IC used for?
An IC is used to perform specific electronic functions such as amplification, timing, data storage, or logic operations. It replaces multiple discrete components with a compact solution.
How are digital integrated circuits different from analog ones?
Digital integrated circuits operate with binary data and include logic gates, counters, and microcontrollers. Analog ICs work with continuous signals and include amplifiers and voltage regulators.
What is the function of a timer IC?
A timer IC, such as the 555 timer, generates time-based events like delays, oscillations, or pulse generation in electronic circuits.
Is the LM3914 still used today?
Yes, the LM3914 remains in use, especially in visual analog display systems like battery monitors and audio meters.
What makes a field programmable gate array unique?
An FPGA allows developers to program and reprogram its logic structure after manufacturing, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and custom digital applications.
Conclusion
Integrated circuits are the backbone of modern electronics. From simple timer circuits to complex programmable logic devices, ICs make electronics compact, reliable, and efficient.
Learning about components like the 555 timer, LM3914, and field programmable gate arrays opens the door to countless possibilities in circuit design and innovation. Whether you’re a beginner or a hobbyist, understanding what an IC is and how it works is a crucial step in your electronics journey.
To learn more about the essential parts used in electronics projects, including other useful ICs and semiconductors, visit our Components category.
